Which panel voltages are typically preferred and why?

Choosing the Ideal Solar Panel Voltage for Your System: 12V, 24V, or Higher
Selecting the ideal solar panel voltage is essential for building an efficient and compatible solar power system. The voltage you choose affects how well your panels integrate with inverters, batteries, and other components, influencing efficiency, scalability, and installation costs. Here’s a breakdown of the most common options—12V, 24V, 48V, and high-voltage panels—and their ideal application
12V Panels
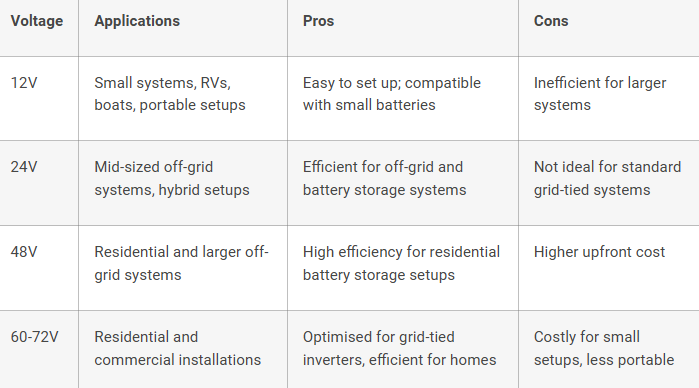
Best For: RVs, boats, small off-grid cabins, and portable systems.
12V panels are perfect for small-scale, portable solar systems. Commonly used in mobile setups like RVs, boats, and camping gear, they’re also suitable for off-grid cabins with low power requirements and 12V battery systems.
Why Choose 12V Panels?
Compatible with small 12V batteries and DC appliances.
Easy to install and handle for low-power applications.
Ideal for portable and mobile setups.
Drawback:
Not efficient for larger systems, as they require multiple panels in series to meet higher power needs.
24V Panels
Best For: Mid-sized off-grid systems, hybrid battery systems, remote locations.
24V panels are widely used in mid-sized solar setups, powering remote cabins, homes, or off-grid systems with moderate energy demands.
Why Choose 24V Panels?
More efficient than 12V systems for medium-scale applications.
Compatible with 24V battery banks, which are more efficient than 12V systems.
Suitable for areas with limited grid access.
Drawback:
Less practical for large residential or commercial systems requiring higher efficiency and compatibility with advanced inverters.
48V Panels
Best For: Large off-grid systems, residential setups with battery storage, and some commercial applications.
48V systems are ideal for high-energy applications, offering a balance of efficiency and compatibility. They’re commonly used in residential setups that incorporate battery storage.
Why Choose 48V Panels?
Improved Efficiency: Minimizes current loss over long distances.
Battery Compatibility: Designed to work seamlessly with modern 48V battery banks.
Inverter Compatibility: Many inverters for residential and small commercial systems support 48V configurations.
Drawback:
Higher initial costs due to specialized components, but the benefits outweigh the expense for high-consumption homes or battery-focused systems.
High-Voltage Panels (60V to 72V)
Best For: Residential rooftop systems, commercial installations, utility-scale solar farms.
High-voltage panels, often described by cell count (e.g., 60-cell or 72-cell), are the standard for residential and commercial grid-tied systems. Operating at 30–40V per panel, these panels can scale to 300V or higher when connected in series, enhancing efficiency.
Why Choose High-Voltage Panels?
Efficiency: Reduces energy loss over long distances (e.g., rooftop to inverter).
Compatibility: Works seamlessly with most residential and commercial inverters.
Scalability: Easily expandable by connecting panels in series.
Drawback:
Integration with battery systems can be more complex and costly, though advancements are improving compatibility.
Summary: Choosing the Right Solar Panel Voltage
12V Panels: Best for small, portable applications like RVs or camping setups.
24V Panels: Ideal for mid-sized off-grid systems and remote locations.
48V Panels: Excellent for residential systems with battery storage, balancing efficiency and compatibility.
High-Voltage Panels: The top choice for residential and commercial grid-tied systems due to efficiency, scalability, and inverter compatibility.
By understanding your energy needs and the specific demands of your system, you can select the right solar panel voltage to maximize performance and meet your goals effectively.
Get in Touch with Us
TALK TO OUR EXPERTS
See how much you can save with solar energy
